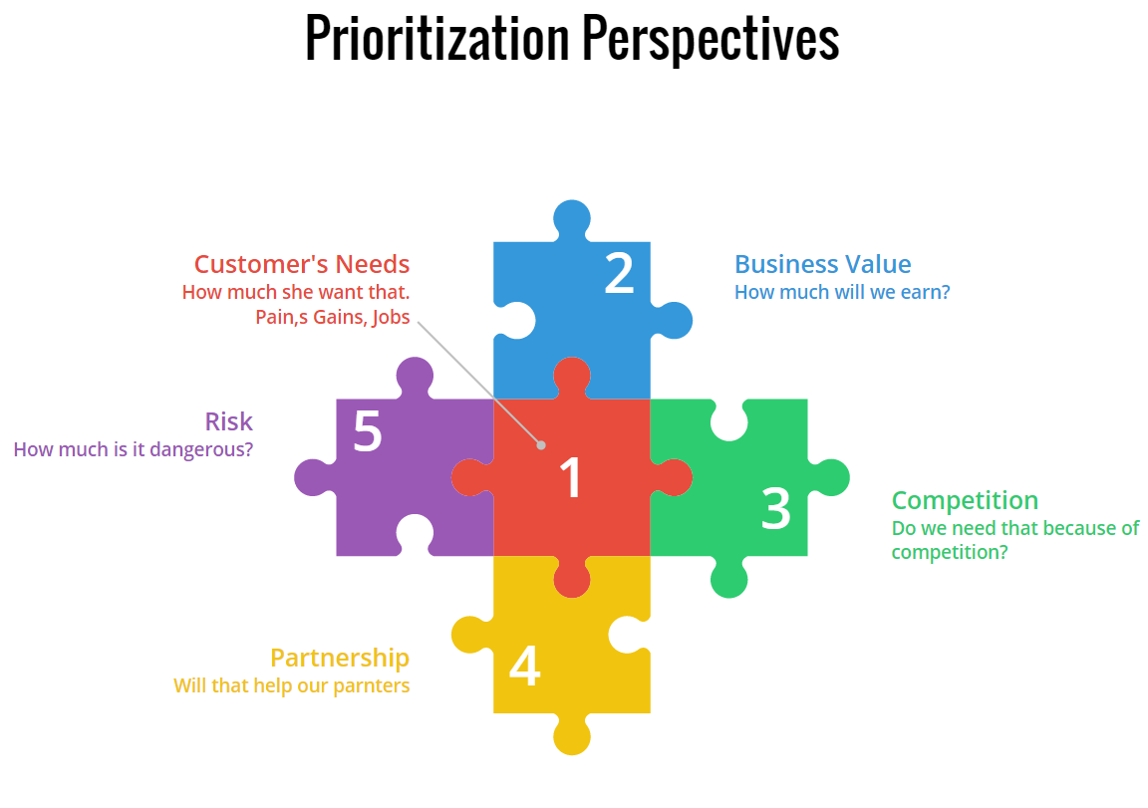
The first blog post about prioritization was focused on MoSCoW – prioritization of the backlog from the perspective of customers. This is not enough for the products development of the commercial company. You need to survive, to pay bills, to pay the next sprints. You have to think about features from the perspective of the company as well. You should consider the business value in your Agile prioritization.
Business value in Agile product
Prioritization by business value, not just in Agile, is however tricky. Many software development teams fail at it. For most companies, this is the most abstract part of the agile coaching sessions we do for our clients. The reason is very simple. Many companies struggle with an understanding of the business model of the company. Most of them even do not have such a business model for the products defined. That leads to a big failure. Earlier or later product will not be successful hence it is going to die. Not worth investing in, nor 1 Euro.
The reason is very simple. Many companies struggle with an understanding of the business model of the company. Most of them do not even have such a business model for the products defined. That leads to a big failure. Earlier or later product will not be successful hence it is going to die.
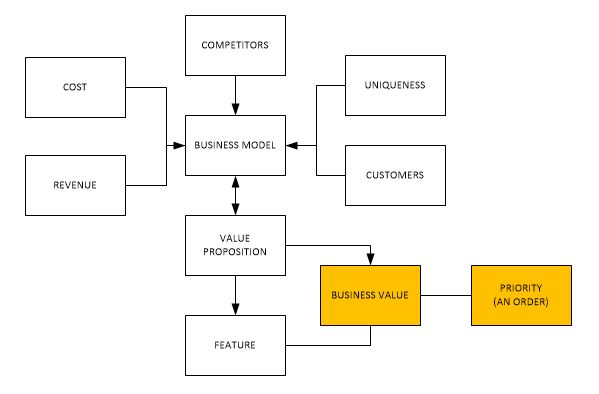
The final order of the requirement is an outcome of a thoughtful thinking process starting far away from feelings. As first, we need to describe the business model.
The most common are traditional business model documents with vision, strategy, business forecasts, cost structure, etc. You can find dozens of such templates on the Internet. For us, they are not worth an agile environment as you will need to react to a lot of changes and they are quite huge. Resistance to changes, hard and slow to evaluate.
Business Model Canvas
Business Model Canvas puts all necessary information on one page. Business is described from multiple perspectives which should be easy to validate on any day of the product delivery. Some parts of it do even describe customers in more detail (see Value Proposition Canvas) which can be then used in product backlog management to describe personas used in user stories.
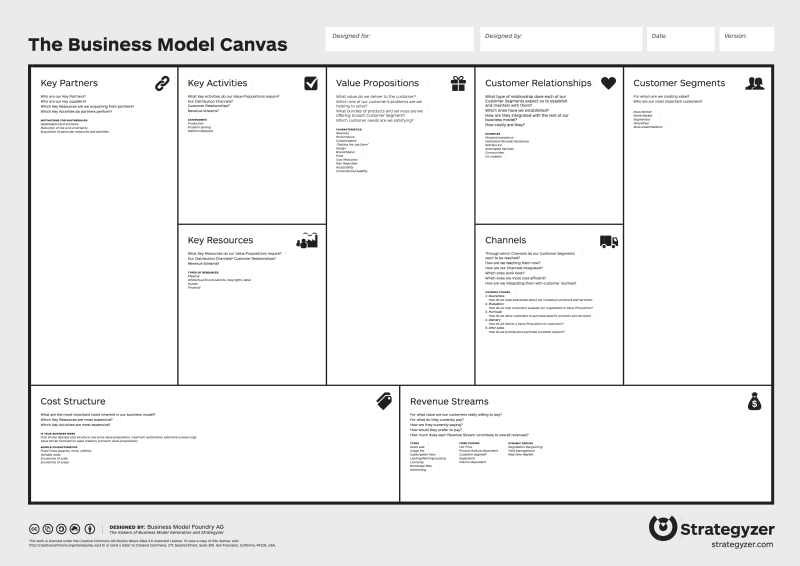
Lean Canvas
The Lean Canvas is a simpler version of the Business Model Canvas whilst still providing all necessary information. It’s a better fit for small products where you do not need to describe for example partners.
Business value types
The value of the business is of different types:
- New income – the feature, idea, will help gain new customer segments.
- Incremental income – the feature, idea, will help increase the number of customers in already identified customers segments.
- Effectiveness – the idea will help save cost or speed up the delivery of future features.
- Investment – the idea, once implemented in the future, helps grow the business.
Additional tips for business value types are the return of investment, turnover, profit, capitalization, customer relationship, reputation, brand.
Perspectives of the business value
Business value in Agile product development can be represented just by one value. Which is not easy. Is business value based on the number of charged licenses? Total revenue? What about investments in research? What about quality? What about technology research and technical debts? What about strategy and vision?
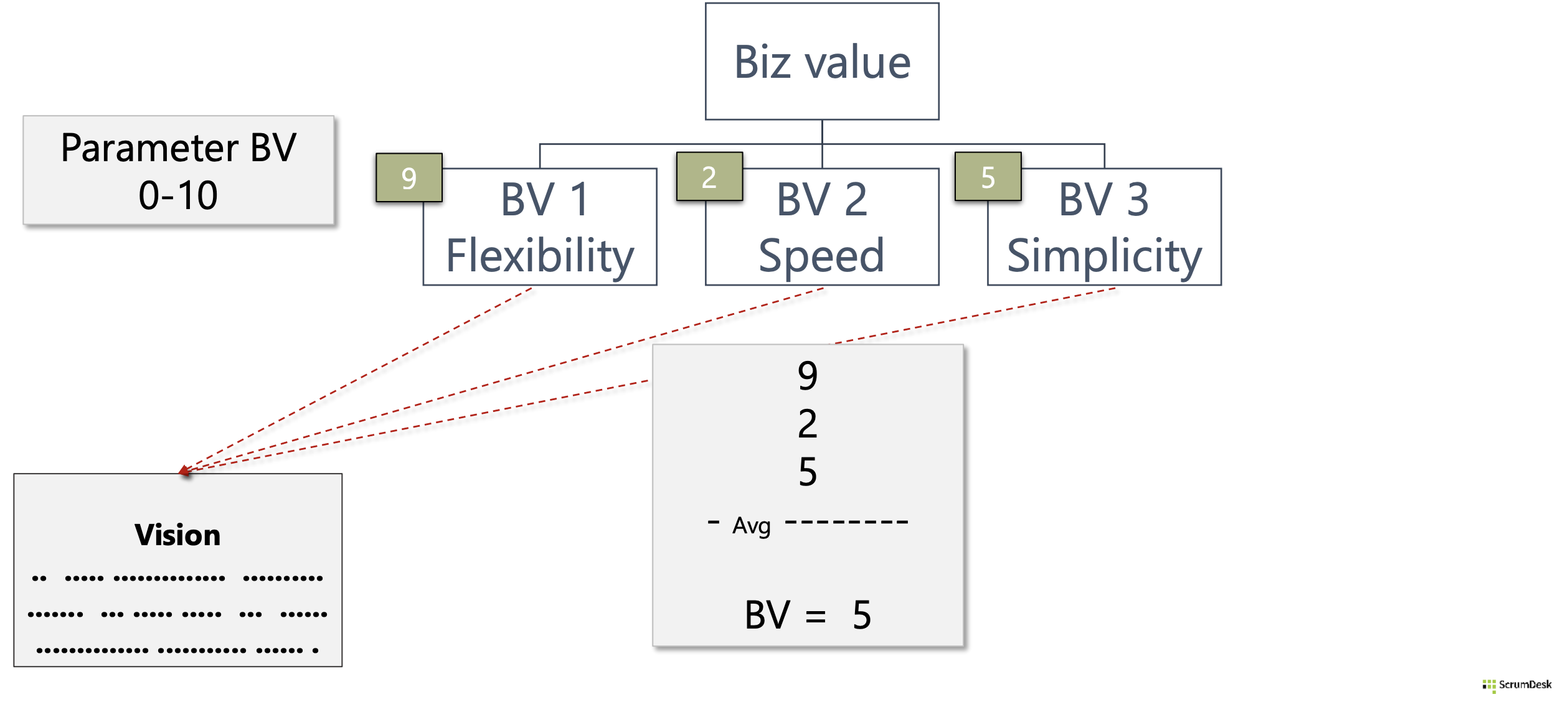
Hard to answer by one value. Therefore it makes sense to think about parts, and perspectives, of the product’s business value. What should be considered, and what is not so important? Consider vision, strategy, competitors, technology, investments, etc. It is not necessary to have too many perspectives. 3-5 is practical.
Tip: Prioritization by business value starts with prioritization of business value perspectives.
Simple estimation of the business value
At the ideation stage, it is not necessary to any fancy perfect business value analysis. Ideas are high-level and therefore is not necessary to do deep math about the business value. In Agile, it is preferred the principle As Late As Possible. For the first prioritization, the relative comparison is enough.
For that use just Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. Enter business features into rows. Columns represent selected parts of the business value. Now focus on one perspective (column). It helps to hide others to be more focused.
For values use either T-Shirt sizes (XXL, XL, L, M, S, XS), or use the Planning Poker (story points) scale. That is even more practical later on, but not necessary in the first few iterations. Once you completed the estimation, hide the currently estimated business perspective and switch to another perspective.
It helps to have a Total Business Value column with a formula that summarizes perspectives. That might be just a simple sum of business perspectives, or it might be even a weighted sum of business value perspectives. Weights are usually agreed upon by senior management to follow the business strategy.
How to manage business value in ScrumDesk
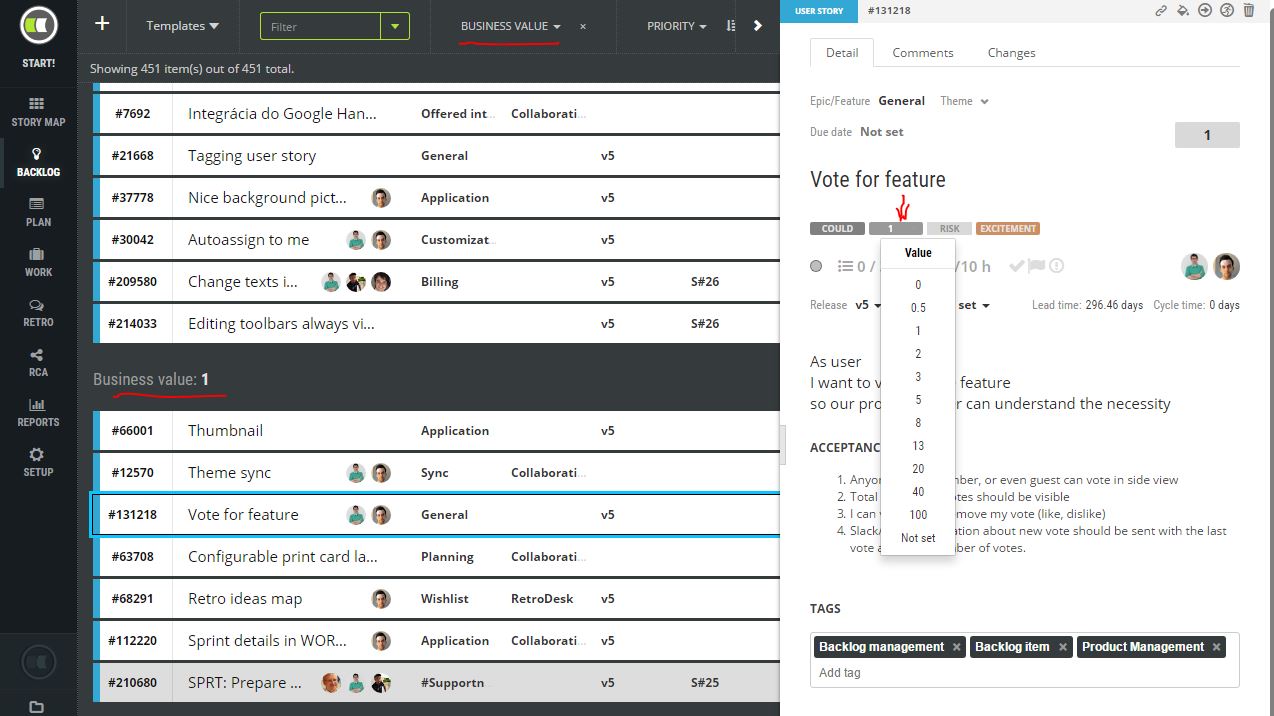
Based on your business model you will be able to specify the business value provided by features (user stories). As is typical in Scrum, the business value is often a relative comparison of the values of different requirements. In ScrumDesk we offer a planning poker scale for business value parameters.
Business value can be entered in the side view available once you click some user story cards. Except for the planning poker values, it is possible to enter other values as numbers as well. Some of our clients prefer to evidence the real business value as a feature’s revenue.
Some other customers prefer to use just T-Shirt sizes (XL, L, M, S, XS).
This value can be used later for filtering, sorting, and ordering of requirements in STORY MAP, BACKLOG, PLAN, or WORK view.
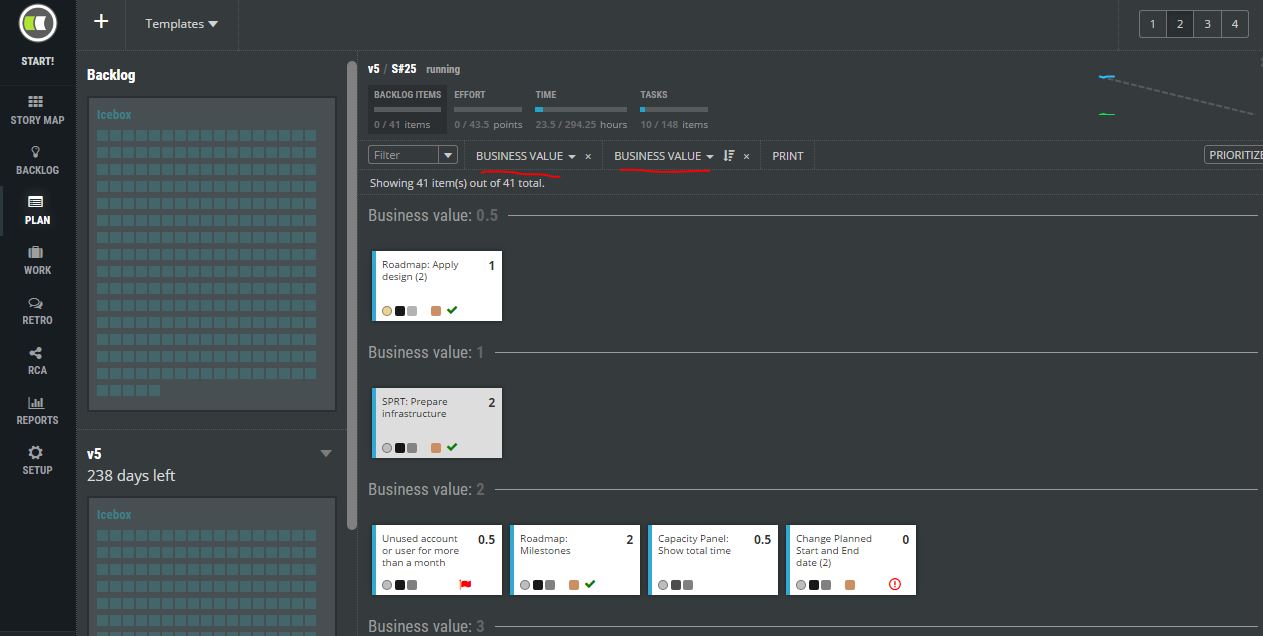
How to mix MoSCoW and business value?
In the previous article, we mentioned that you should start to prioritize requirements from the perspective of the customer. We ended up with the list of cards in the order of values Must, followed by Should, and then Could.
Now, having business value as well, we can update the order with business value as well.
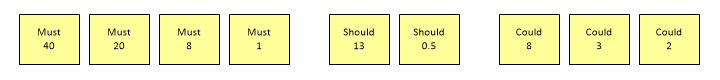
The prioritization can be done by the Product Owner and stakeholders, or ideally together with the development team to get feedback early.
Evaluate delivery of the business value
Once features are done, the business value is added to the product. That is tracked in the Business value chart on the Reports page.
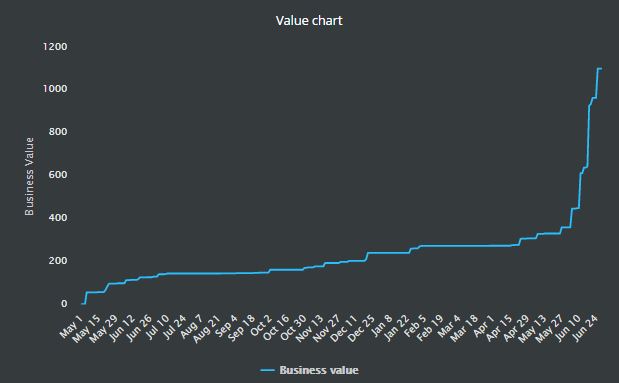
MoSCoW values created segments that were ordered then by business value.
However, if you want to be sure about your priorities in the backlog, you should consider risk level as well.





